|
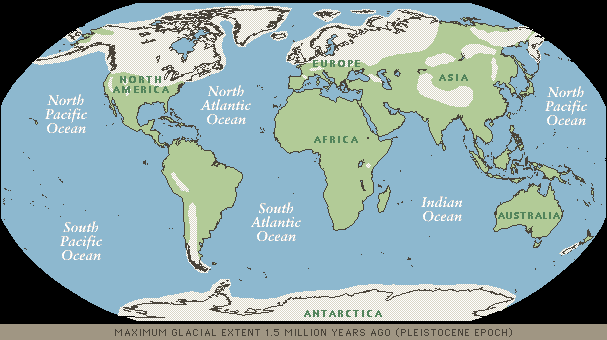
| Extent of Glaciation during the Pleistocene |
|
| images.encarta.msn.com/.../maps/map/T041365A.gif |
Global Conditions
During this period, global temperatures rapidly fluctuated between warm and intensely cold (8). These would have
been great conditions in which for glaciers to form; in such, large ice sheets began to cover northern North America and Europe
(8). During this time, sea levels around the world had dropped as much as 450 feet, which is evident by the exposure of shoreline
deposits and shells at the edge of the continental shelf (7).
This period is characterized by very distinctive large
mammals such as mammoths, mastodons and sabre-toothed tigers, but they all went extinct by the end of the Pleistocene. A reason
for this just may be the climate and their inabillity to acclimatize themselves to the major weather shifts (3). Climate records
from this period have been preserved for us by fossils including diatoms and corals (7).
Theory of Glacial Ages
"At times in the past, colder climates prevailed during which much more of the land surface of Earth
was glaciated than at present" (6)
Possible Causes of Glaciation
During the Pleistocene there were 4 major glacial events in addition to several other minor events,
which were all separated by interglacial periods (11). We have also theorized that Milankovitch cycles could have
been a cause of these glacial events. Milankovitch cycles are periodic variations in solar radiation on Earth which are caused
by the sum of many repeating changes in the Earth's motion (11). A second, and more recent theory, is that a glacial cycle
is determined by the time it takes for the ocean to go through one major heating/cooling cycle (1). For the time being, we
will explore all possible factors for the Great Ice Age:
Accumulation of Ice: This process
of ice accumulation has taken place over several points in geologic time. As ice formation proceeds at a faster rate than
melting, glaciers had a chance to grow to larger sizes over time. (4)
Circulation of Water
and Moisture: One theory discussed by Cornwall (1970) is that an uplift of Panama Isthmus, which were previously volcanic
islands, had prevented warm water from leaking into the Pacific Ocean. A stronger North Atlantic Drift was sent in the North-East
direction and this circulation just may have reached the Arctic Ocean. If so, the moisture-rich winds would have hit
the cold, higher ground of the northern land masses, resulting in heavy snowfall and glacial growth. (4)
Extra-terrestrial
influences: Solid bodies from space which were captured by Earth's gravity usually are burned up even before they reach
the surface of the planet. The dust formed will eventually drift towards the Earth's surface. However, some meteorites can
get through the atmosphere and can be quite large, able to make an impact on Earth (4). The extreme pressure from an impact
would have melted rocks on the Earth's surface and created a great cloud of dust or smoke which would have blocked out
the sun (2). This would have disturbed ocean circulation and started a cycle of global ice ages (2).
Other Influences include:
- Atmospheric composition (concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide)
- Plate
Tectonics (position of the continents)
- Variations in solar output (including heat and radiation)
- Eruptions
of super volcanoes (which could influence global temperatures)
(10)
| click to see bbc news story on meteorite impact |

|
| news.bbc.co.uk/.../images/_233199_mglass180.jpg |
Evidence for the Great Ice Age
There are 3 main types of evidence for ice ages:
1. Geological-
striations carved in rock, glacial moraines, valley cutting, and till despositions (which we have previously discussed).
2.
Chemical- variations in the ratios of isotopes in sedimentary rocks, ocean sediment cores and ice
cores. [Remember about radiocarbon dating and its ability to give us the age of rocks by knowing the half-life of carbon-14 and
by measuring the remaining percent of isotope in the rock]
Weart (2006) gives an example of chemical evidence in his
article, where in 1947, a nuclear chemist, Harold Urey, discovered how to measure ancient temperatures by measuring the
oxygen built into fossil shells from the sea floor. The amount of oxygen isotopes taken up by an organism from the sea
water varied according to ocean temperatures at the time (9). Therefore the ratio of O18/O16 served as a kind of "thermometer"
(9).
3. Paleontological- changes in the geographical distribution of fossils.
(10)
| Fossil Evidence |
|
| http://www.berkeley.edu/news/media/releases/2004/09/30_.shtml |
Click the picture (left) to read about how climate change and human pressure caused large mammal
extinctions in late Pleistocene
|

